Humidity
Source: Calculator.net
Humidity is defined as the amount of water vapor (gaseous phase of water) in the air. It is an indicator of the presence of dew, frost, fog, and precipitation. The maximum amount of water vapor that can be held in air is affected by temperature; the higher the temperature, the greater the amount of water vapor air can hold before reaching saturation.
Humidity is often discussed in terms of absolute humidity and relative humidity. The value for absolute humidity is returned as part of the results of the calculation, but it is relative humidity that is widely used in everyday life and is used as part of the calculation of dew point temperature.
Absolute humidity is the measurement of the water content in the air, typically in units of grams per cubic meter. It is calculated by dividing the total mass of water vapor by the volume of the air. Given the same amount of water vapor in the air, the absolute humidity does not change with the temperature at a fixed volume. If the volume is not fixed, as in the atmosphere, absolute humidity changes in response to the volume changes caused by the temperature and pressure variation.
Relative humidity compares the current ratio of absolute humidity to the maximum humidity for a given temperature and expresses this value as a percentage. The higher the percentage, the higher the humidity. It is affected by both temperature and pressure. Given the same amount of water vapor, there will be a higher relative humidity in cool air than there is in warmer air.
Relative humidity is a commonly used metric in weather reports and forecasts and is a good indicator of precipitation, dew, frost, fog, and apparent temperature. Apparent temperature is the temperature perceived by humans. In summer, the higher the relative humidity, the higher the apparent temperature. This is a result of a higher humidity reducing the rate at which sweat evaporates, which increases the perceived temperature.
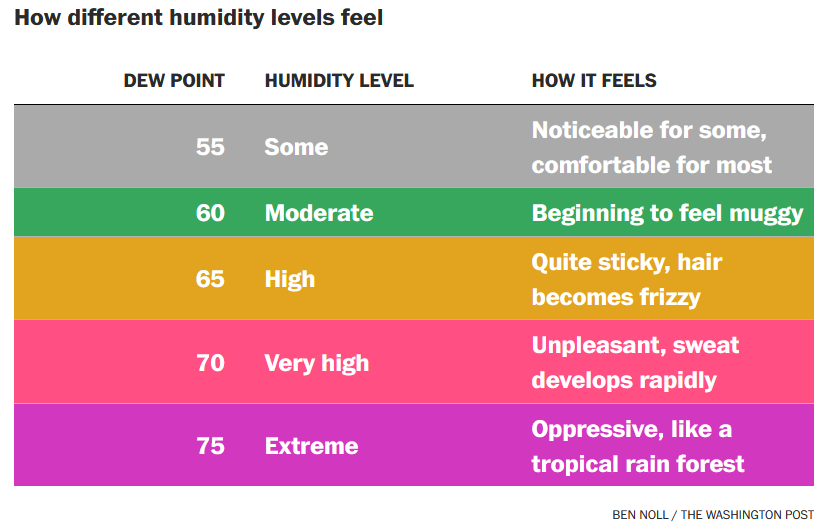
A relative humidity of 100% indicates that the air is saturated, meaning that given the current conditions, water vapor in the air cannot increase further in normal conditions. 100% relative humidity is also the point at which dew can begin to form. See also Dew Point.
Here is a link to a humidity calculator.
The reason the air gets dry in winter in your home is that cold air is dry air - and that cold air leaks into your home. Basically, the cooler the air, the less moisture it can hold.

Ideal humidy levels inside your home are shown below:





